I’m often asked, what do you mean by sustainability? While there are many definitions available such as the one from Brundtland: “Meeting the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs”.
The issue is that sustainability is such a vast concept that the available definitions of sustainable development don’t always satisfy people’s need for details. However, understanding this concept gets much easier when we start considering the 3 E’s of sustainability! But, what are the three e’s of sustainability?
Key Takeaways
- Balances economic growth, social equity, and environmental protection.
- Encourages sustainable actions in businesses and communities.
- Fundamental for achieving long-term global sustainability goals.
What are The 3 E’s of sustainability?
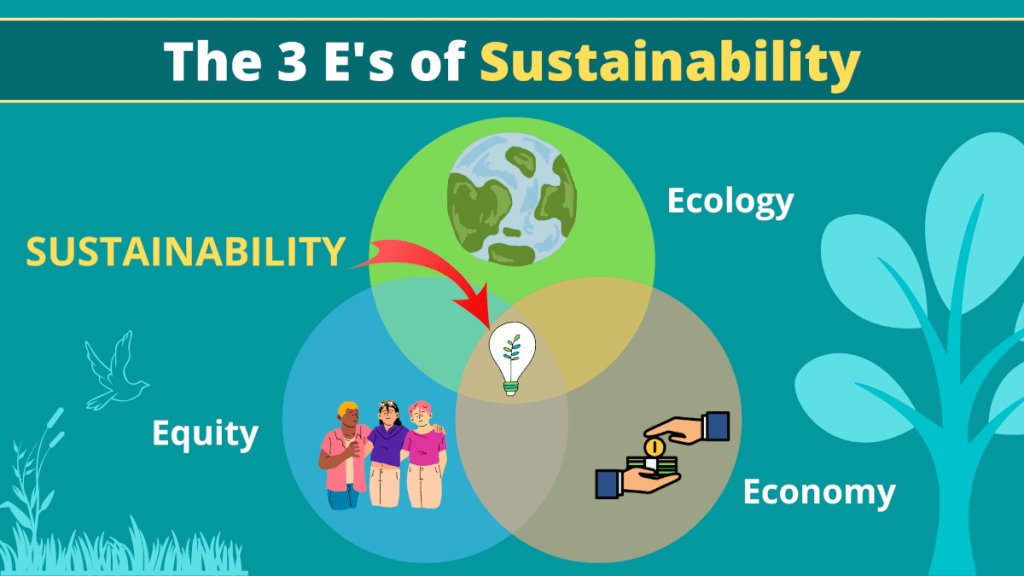
The 3 e’s of sustainability are Economy, Ecology and Equity. To achieve sustainable development the three Es of sustainability need to be in balance between each other. This means that sustainability is achieved when your actions are helping to develop the economy, promoting social equity, and protecting the integrity of the environment for future generations.
The three E of sustainability are also known as the 3 pillars of sustainability (the 3 Ps), or triple bottom line of sustainable development. Another similar framework but more focused on the human aspects are instead offered by the 4 pillars of sustainability model, which requires also more specific human factors to be properly balanced in order to achieve sustainability.
The three E’s of sustainable development are offering a very useful framework to operationalize our sustainability efforts. Thanks to the 3 Es it is easier to understand what practical actions we should take to be more eco-friendly.
The concept goes hand in hand with the 6 Rs of sustainability framework, which serves a similar purpose but it is more specific to actions we can take in everyday life. The 3 E of sustainability are the foundations of the ideas expressed by the 6 Rs.
Economy
Economic development is a broad concept, however, from the sustainable development point of view, it can also be referenced as economic sustainability.
Economic development in sustainability means that a business must be profitable to be sustainable. This will allow the company to create jobs as well as useful products and services to satisfy human needs.
However, bear in mind that economic development should be balanced with the other E’s of sustainability. So to be sustainable, a corporation should not pursue profit disregarding equity and environmental protection.
This is how economic development in sustainability is fundamentally different compared to traditional economic growth, where profit was the main (and sometimes the only) driver.
It is only with economic development that we can have the necessary resources to satisfy basic human needs such as food, healthcare, and shelter. The key difference is that economic growth should be mindful and not harm people or the environment.
For example, consider those issues around economic development sustainability:
- Fairtrade: do workers have adequate salaries?
- Are workers operating in a healthy and safe environment?
- Eliminate child and captive labor
Those and many other considerations should be made by business leaders when assessing the economic sustainability of a specific activity.
Ecology
Ecology means environmental protection and integrity and it is also known as environmental sustainability. It refers to all the practices we need to adopt in order to conserve the environment.
This includes things such as being environmentally mindful of our actions, managing the demand for natural resources as well as actively managing them.
This means considering if any action we plan to take is going to have a negative impact on the environment. For example, you should ask yourself those questions:
- Is this going to pollute the air to the point that it is likely to harm people’s health and well-being?
- Is it going to degrade the available natural resources to the point that they can’t come back?
There are many remarkable examples of this which are worth reading about, however, in general, those are using 2 different types of activity:
- Environmental management – Use environmental science and conservation biology to actively manage the allocation of natural resources. Taking into account the capacity of the ecosystem to absorb the impact of human activities.
- Demand management – Influence the demand for natural resources by leveraging green technology, government incentives and regulations, and promoting environmental awareness and an eco-friendly lifestyle.
Those include things such as sustainable forest management, zero waste policies, sustainable water management, sustainable agriculture, and much more.
For example, for environmental protection in sustainable agriculture, we would be looking at things like:
- Using water efficiently
- Minimizing emissions of greenhouse gasses
- Minimizing the use of nonrenewable energy
- Use fewer chemicals or avoid them altogether, especially synthetic chemicals
Equity
Social equity is also known as social sustainability and it is perhaps the less known aspect of sustainable development.
Social equity (social sustainability) aims at satisfying basic human needs and rights, as well as enhancing the living conditions and providing equal opportunities for everybody in the economy and society.
Social wellbeing is a notion that often gets a lot of attention today. There are several ideas that account for social wellbeing. For example, social wellbeing is influenced by the following elements:
- Health
- Personal relationships
- Peace and safety
- Living standards
- Equality
- Freedom
- Achievements
- Environment and services
- Prosperity
The idea of equity and social sustainability is not just about providing for social wellbeing. It’s about sustaining a good level of it nand granting equal opportunities for everybody. This includes things such as:
- Equality
- Understanding others
- Inclusion
- Equal opportunities
- Individual empowerment
For example, when looking at social equity and issues we could be asking ourselves those type of questions:
- Is food affordable for everybody?
- Is food easily accessible?
- Are there equal opportunities for social minorities?
- Is there any type of social discrimination?
- Are there ways to socially develop communities and relationships?
- Is the city developed with sustainability as a priority? Are there any green areas to socialize? Are the buildings using the latest smart technologies?
There are many other examples of this, such as quality education, childcare, senior care, good healthcare, fighting poverty, and much more.
All of those considerations are crucial for human wellbeing and equity in society. Because it is not possible to reach sustainable development without inclusive and vibrant social communities.
Why are the three E’s of sustainability important?
The 3 Es of sustainability is important because they allow people to better understand the practical actions they need to take to move towards sustainable development.
The three e’s of sustainability are not just theory, but they are a practical framework that can be used to properly balance every aspect of sustainable development, reaching that sweet spot where there is economic growth coupled with social equity and environmental protection.
The three Es of sustainable development are so important that in the last decade they have been used extensively to evaluate the social and environmental responsibility of businesses. And more recently to develop the ESG metrics and financial scoring system for companies.
Finally, the 3Es of sustainability has been the basis to write the UN sustainable development goals (SDG) for 2030. This is a set of important goals we should aim for in order to reach sustainability in all of its forms by 2030.
Given the importance of sustainable development for our future and the future of our planet, everybody should know what the 3Es of sustainable development are and start applying them in their lives.
Conclusion
Here’s quick summary of the meaning for each of the three Es of sustainability:
- Economy: while a business needs to be profitable, economic growth should be in harmony with human and environmental needs.
- Ecology: environmental protection and integrity are essential for long-term sustainability. This includes things such as: limiting the use of natural resources, giving preference to renewable energy, reducing unnecessary consumption, reducing waste, and increasing recycling.
- Equity: social equity is vital for human wellbeing and long term sustainability. This includes things such as peace, health, freedom, equality, inclusion, and individual empowerment.
By carefully balancing those 3 aspects of sustainable development we will be able to create a new and better society that cares about the environment and human needs as much as it cares about economic growth!

