Do you remember the carefree years in the past when people and businesses didn’t care much about the environment? Luckily those days are now over and I can see new exciting green technology examples popping up almost every day!
What is green technology?
Green technology is the use of technology for eco-friendly purposes, like for example reducing energy consumption, reducing waste, and protecting the environment. This means any product, design, formula, algorithm, procedure, method, discovery, process, technique, idea, know-how, or software that can help us reduce our environmental footprint and ultimately achieve sustainable development.
Green technology examples and their benefits
Here are 14 great sustainable technology examples. Those Examples of environmental technology can help us shape a green future.
1. Solar panels

What example of green technology absorbs light and converts it into energy?
Solar energy has many benefits for the environment and is a renewable source that can be harvested in many different ways. The most popular of those are solar panels.
Solar panels can be of 2 different categories: thermal to produce hot water or photovoltaic to produce electricity.
Thermal solar panels are very simple, they have a tube running inside the panel and covering the entire surface. The tube and the interior of the panel are painted a black color to absorb more of the solar radiation, while the cover is kept transparent to allow the sun to shine directly inside and create a greenhouse effect. When the sun shines, the water running inside the pipe gets hot and is stored in a thermal tank waiting to be used.
Thermal solar panels are very efficient in making hot water, and just 2 of them are enough to satisfy the needs of a single-family home!

Photovoltaic (PV) solar panels are more complex and, thanks to the properties of the materials they are built with, they can convert solar radiation directly into electricity, without the need for any moving part.
The energy produced with PV solar panels has a carbon footprint 93% lower than gas and during their lifetime they produce 30 times the energy that was used to produce them.
Solar panels can be recycled (mandatory in the EU) recovering about 90% of the materials used for their construction. However, solar panel recycling is not so common around the world yet, so, unfortunately, some of those materials are still going to waste in unregulated markets.
The problem of PV panels recycling is a bit chicken and egg: there aren’t yet enough old solar panels disposed of to make recycling economically viable. However, this is going to change in the coming years while a growing number of older installations will have to be replaced.
Solar panels are an amazing green technology example that can increase home value and is helping the world to achieve important goals, reducing the need for fossil fuels and, as a consequence, reducing their environmental impact.
If you are considering solar, make sure to review the best questions to ask a solar company before signing a contract!
Finally, solar panels can also be used to make yachting more sustainable. In fact, in recent years a number of solar catamarans started to become available in the market. All thanks to solar panels, which give them an unlimited range without relying on fossil fuels.
2. Sustainable water purification

Water is abundant on our planet, however, only 3% of it is freshwater good for drinking. This makes drinking water a very scarce and precious resource that governments and international organizations, such as the United Nations, are striving to preserve. Water scarcity is a growing problem all over the world.
Using a home-based water purifier for an off-the-grid system or to filter tap water is the most sustainable drinking water solution for households. But on a larger scale and when starting the process from dirty water, the currently available technologies for water purification use quite a lot of energy and are not very sustainable.
For this reason, new water purification technologies are under development, and in several years we may be able to tackle the world drinking water issue more sustainably.
One of the most promising and cutting-edge green technologies for water purification was recently published by Nature and it is based on protein nanofibrils.
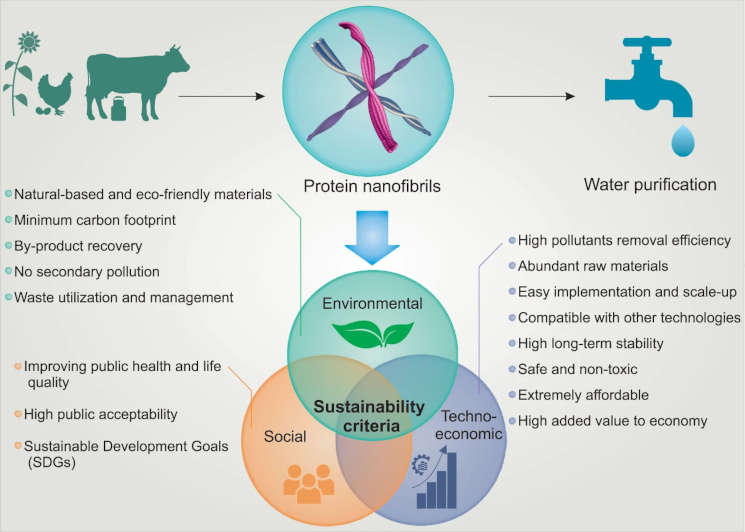
The potential benefits of this technology are:
- Reduced waste because it is possible to use diary and agricultural industry byproducts, or even food waste to create the protein nanofibrils (ie. the water filter)
- Effective filtration system
- Low carbon footprint, because the contaminants are naturally absorbed from the water rather than forcibly removed, so they require much less energy
- Affordable and scalable
- It can satisfy all the three pillars of sustainability and become a solution to achieve sustainable development in the water purification sector
This is indeed a very promising green technology for sustainable water purification.
More research is still ongoing to further develop this technology and also to manage the sustainable disposal of the used water filters.
3. LED lighting

LED lighting experienced rapid technological advancement and adoption during the last decade. This is because LED lights are extremely energy efficient and the perfect eco-friendly replacement for traditional bulbs.
LEDs lighting is an interesting example of sustainable development that brings a number of distinct advantages:
- Exceptionally long life span (over 30 years if used 4h per day)
- LEDs use 85% less energy
- Reduced maintenance costs
- Improved safety
Finally, when technology gets mass adoption, its costs tend to go down thanks to the economies of scale and increased competition in the market. For those reasons, the cost of LED lighting dropped significantly in the last decade.
Considering the pros and cons of LEDs, and the competitive prices, it is no surprise that LEDs are becoming the preferred lighting solution. The good news is that they are much more sustainable than traditional lighting too!
Lighting is responsible for about 15% of your home’s electricity consumption, and considering the current energy costs, LED lighting is an investment that is paying for itself quite quickly. Especially considering the recent skyrocketing energy price inflation.
LEDs are an amazing example of a mature and affordable green technology. They can be used both outdoors and indoors, where they can also be solar-powered. They are being used in a great variety of settings: automotive, traffic lights, indoor vertical farming, and much more.
4. Vertical farming and hydroponics

Vertical farming and hydroponics are other examples of green technologies that are improving our agriculture in so many ways.
Thanks to this technology is now possible to consistently produce large quantities of quality food, also where the weather or space would not normally allow it. But how are those technologies working?

Vertical farming is exactly as the term suggests: the plants are grown vertically and stacked in special columns or shelves. The technique allows for growing large amounts of food in a limited space and controlled climate.
Hydroponics is a technique that consists in growing the plants in the water or on an inorganic substrate. The system will be placed in a closed environment that could be with or even without windows. If there is no natural light, LED lighting will be used instead. The plants are then fed mostly with artificial nutrients, but at the same time, they don’t need any pesticides because of the controlled environment.
Hydroponics and vertical farming can be combined to produce food even inside urban areas with no land and no natural light. This allows having a local source of food also in the cities, reducing the need for transport. For example, an increasingly successful application of those technologies is the farming of microgreens for local restaurants.
A big advantage of vertical farming and hydroponics is the limited need for water, those systems are in fact only using about 10% of the water normally necessary for traditional agriculture! This is a very important factor when evaluating the sustainability of vertical farming and hydroponics.
In recent years another variation of hydroponics has also been growing in popularity: aeroponics. There are a number of advantages and disadvantages when considering hydroponics vs aeroponics farming. However, aeroponics in general more efficient but more expensive to set up.
Finally, those farms require much less work compared to the traditional ones, because the plants are already in a comfortable place for the harvest and there is no need to plow the fields.
5. Biogas

Biogas is eco-friendly methane produced from natural and renewable sources. Biogas is produced by anaerobic digestion, a process during which organic waste is decomposed by microorganisms in the absence of oxygen.
Turning your household’s organic waste into clean biogas for your home is possible. However, at the moment this technology is mainly used on farms, where they have more organic waste to deal with.
The technology can be quite interesting also for off-grid homes.
This amazing green technology example is reducing the methane emissions normally generated from organic waste.
Turning waste into renewable energy for your home or business and producing a nutrient-rich fertilizer that can be used to grow food and other plants.
6. Plant-based protection for fresh produce

Nearly half of the fresh fruit and vegetable produce is wasted every year, this is a huge problem for sustainability, but thanks to plant-based food protection technologies this reality may be about to change!
This protective material is made of a blend based on fruit and vegetables’ peel, and seeds to create a special protective layer that can be applied to fresh produce to increase its natural shelf life.
The benefits of this plant-based protection for fruit and vegetables are:
- Increased shelf life by reducing oxidation and keeping moisture in
- It’s made with materials that we usually eat in our diet
- Less wasted food: with a longer shelf life, food is less likely to go bad along the supply chain
- It’s invisible
This amazing green technology example allows us to reduce food waste: one of the things that make us feel somehow guilty as soon as we learn how much of it is wasted along the supply chain (that is up to 45% of it).
7. Wind Energy

The wind is a renewable energy source that doesn’t cause carbon emissions, is plentiful and readily available. Wind turbines are the green technology used to sustainably convert the wind’s power into electricity and they can also be installed offshore, without occupying any land and out of sight.
How are wind turbines working? Here are the main steps to converting wind into clean electricity:
- When the wind is blowing, the wind turbine spins due to the aerodynamic forces generated by the airflow on its blades.
- The turbine blades are connected to the main shaft that rotates with the blades.
- The main shaft is also connected to a gearbox that is transferring the motion to an energy generator (alternator).
- The produced electricity goes to a transformer to match the voltage of the power grid and is then made available to be used
Wind energy has many pros and cons. The main disadvantage of wind energy is its intermittency: if the wind is not blowing, you don’t get any power. For this reason, the power generated from wind farms, if not immediately used, may be stored in batteries.
Nowadays wind turbines of any size are available on the market, so, if you live in a windy place, you can even put a small one in your backyard or on the roof and cut down on your electricity bill!
The wind turbines installed in recent years are about 30% more efficient compared to the initial models installed in the 80s and 90s. While in the last 30 years the cost to produce wind energy dropped by as much as 94.5%, down from $0.55 to only $0.03 per kilowatt-hour (kWh)! A truly exciting development path for this green technology!
Those results were possible thanks to extensive research and the use of advanced digital technologies such as computational fluid dynamics (CFD). Going more technical here! CFD is a “digital twin”: a tool that allows to simulate and optimize the shape of the turbine’s blades as well as optimizing the placement of wind turbines on a specific site to better capture the power of the wind. The above video is an example of what such simulations look like.
8. Micro Hydro-power Plants

Hydropower was one of the first renewable energy sources to be used to produce electricity. There are many hydropower pros and cons, however, the most important disadvantage was that up to now, building a hydroelectric power plant was a big project, involving dams and expensive construction works.
Dams are very expensive to build and can pose important dangers to the local community.
Dams have also a large impact on the landscape and can change significantly the local ecosystems. So they are not a very desirable solution.
One of the most exciting developments in this green technology is the possibility to install micro hydro-power plants. Those don’t require a dam and can be installed with minimum construction works along or on the bottom of rivers and canals.
Those micro hydropower plants are amazing green technology examples:
- They don’t require a dam and can work even on gentle slopes
- They work 24/7 because the water doesn’t stop flowing at night! While the most common renewable energy systems such as solar panels and wind turbines are intermittent by their own nature
- They require minimum space.
- Decentralized
- Can be used for on-grid and off-grid installations
- Zero CO2 emissions when operating
- Simple construction
- Much lower costs compared to traditional hydropower solutions
- They don’t harm fish
The micro hydropower plants are also using considerably less space per generated kW compared to solar panels. The equivalent solar installation would require more than 12 times the space to generate the same power.
9. Plastic waste catchment systems

Plastic waste ending up in our rivers and oceans is one of the greatest environmental problems of our time.
Many innovative solutions have been developed to catch and remove plastic waste from our rivers before reaching the ocean.
One of those systems involves the creation of a bubble barrier to guide the plastic waste toward a plastic catchment system.
The suspended plastic waste flowing inside the river is lifted to the surface by the bubble barrier, then the curtain is guiding the waste diagonally towards the shore, where it is captured by a special catchment system.
Other systems are instead using nets or other ways to avoid having waste flowing into our oceans.
By the way, recent research is also proposing biological solutions to the problem of plastic waste, like for example plastic eating mushrooms. The interesting part is that some of those mushrooms are also edible!
Those are important examples of green technology applied to keep our oceans clean.
10. Smart power management Systems

Did you know that up to 10% of the electricity you consume is wasted by plugged-in devices (even when you are not using them)? That’s a big problem for both the environment and our pockets!
To solve this issue, new smart power management systems are being developed and deployed in modern smart buildings. Those systems are leveraging artificial intelligence (AI) and data analytics to manage power distribution and automatically cut it completely off when not needed.
The AI (artificial intelligence) of the system will monitor your electricity consumption and usage of each of the plugged-in devices then it can formulate recommendations on how to save electricity.
Those systems are a perfect green technology example!
They also demonstrate how digital transformation technologies such as AI can be applied to save electricity and improve sustainability.
11. Sustainable smartphones

Mobile phones are also posing an important environmental problem, especially because most people are changing their smartphones every other year.
Smartphones can contain a number of hazardous materials like mercury, cadmium, lead, arsenic, and beryllium as well as rare or conflict minerals like coltan.
In recent years a number of companies developed more sustainable alternatives using recycled and fairly sourced materials as well as limiting the use of hazardous substances. Those smartphones have a sustainable product design: easy to disassemble, repair, and built to last.
12. Eco-friendly toothbrushes

Plastic pollution is one of the greatest environmental problems of the modern era and over 1 billion plastic toothbrushes are thrown away every year just in the United States.
About 99% of toothbrushes are made of plastic, a material that takes more than 400 years to decompose and is polluting our land and oceans!
In recent years, a number of eco-friendly toothbrushes have been developed: some made of wood, bamboo, and other materials.
This is an amazing and simple green technology example that allows reducing plastic waste.
Switching to a sustainable toothbrush is a simple step that everybody can do, especially now that alternatives of great quality and design are becoming available!
13. Plant-based packaging

Plastic packaging is one of the greatest contributors to plastic waste and microplastics in our oceans. Wouldn’t be nice to have a sustainable alternative?
Plant-based packaging can be used as an alternative to plastic.
The main criticism towards plant-based plastics is revolving around the need of using land to grow the raw materials needed to create those plastic packaging alternatives. However, new materials are in development and those will use only waste, without requiring to grow specific plants to use for their production.
This is a promising green technology example: trying to turn waste into packaging.
14. Fresh food storage monitoring systems

Do you know that up to 1.3 billion tons of fresh food produce, mostly fruit and vegetables, is wasted every year along the supply chain?
This is a huge problem that is especially upsetting when we consider that hunger is still raging in parts of the world. On the economic side, this is about 680 billion dollars of wasted food every year.
To tackle this problem, new food storage monitoring systems have been developed.
Those systems are monitoring the ripeness of fresh food kept in storage and during transport.
Allowing save up to 45% of food waste by making real-time checks and accurate forecasts about when food will go bad. This information can be used to improve the food supply chain by reducing waste and improving profitability for businesses.
How do those systems work? They detect ethylene and other chemicals released in the air by fruit and vegetables while they become ripe. This allows the system to evaluate the ripeness of the food kept in a warehouse or in a shipping container.
This is a great example of green technology that can improve the long-term sustainability of the food industry.
Conclusions
I hope that you enjoyed my list of 14 green technology examples:
- Solar panels
- Sustainable water purification
- LED lighting
- Vertical farming and hydroponics
- Biogas
- Plant-based protection for fresh produce
- Wind energy
- Micro Hydro-power Plants
- Plastic waste catching systems
- Smart power management Systems
- Sustainable smartphones
- Eco-friendly toothbrushes
- Plant-based packaging
- Food storage monitoring systems
There are many green technology companies delivering those products today that will help us move forward toward sustainable development.
I also wrote about the entire range of green technologies and their benefits. From the more traditional ones, that you can already experience in your day-to-day life up to brand new, cutting-edge research that could solve some of the important sustainability problems of the world.
This is because, with the growing interest in environmental issues and the longer-term 2030 UN sustainable development goals in mind, we are finally seeing the problems of our planet getting the attention they deserve.
The green technology and sustainability sectors are also one of the fastest-growing employment and consulting areas. With increasing opportunities in the sustainable applications of industry 4.0, green technology is much more than a passing trend!


